Solving Duplicate Content & Multiple Site Issues: Best Practices
Duplicate content & multiple site issues are two of the most important considerations for any web developer, online marketer, or company owner. Duplicating existing content on your website can negatively affect both SEO and user experience. Managing multiple versions of a single website can take time and effort.
In this blog post, we will discuss duplicate content, why it matters, and how to avoid such issues. We will also look at multiple site issues in detail with best practices outlined so that you can avoid mistakes that could negatively impact your business.

What is Duplicate Content?
Duplicate content is any content appearing on the internet in multiple places. This can include exact copies of web pages, blog posts, or even text snippets. It can also include multiple versions of the same page, such as mobile and desktop versions.
Duplicate content can be unintentional or intentional; it’s important to understand how duplicate content affects your website and SEO efforts. There are two types of duplicate content, both of which can be problematic:
Why Does Duplicate Content Matter?
The duplicate content may have the following negative impacts.
Search engines like Google have algorithms designed to detect duplicate content and will penalize websites for having too much duplication on their pages. Suppose search engine bots find two identical pieces of information from different sources. In that case, they may choose not to index either source or prefer one based on various factors such as domain authority or relevance.
Google, in general, does not want to rank pages with duplicate content. Google claims: “Google tries hard to index and show pages with distinct information.”
Having duplicate content across multiple sites can confuse users looking for specific information but get conflicting results when searching online.
Additionally, you have multiple versions of the same page with slightly different URLs (e.g., www vs. http). In that case, this could lead to problems with link building and rankings because each URL would be competing against itself for search engine attention instead of being seen as part of an overall site structure that helps boost visibility in SERPs (search engine result pages).
Duplicate content can be a major issue for webmasters, as it can negatively impact search engine rankings and user experience. The next section will discuss why duplicate content matters and how to avoid it.
How to Fix Duplicate Content Issues?
With duplicate content accounting for 25-30% of the web, it’s important to understand how to avoid and resolve such issues.
- Make Sure Your Site Redirects Correctly
Sometimes you have multiple versions of the same page and the same SITE. Although uncommon, I have witnessed it numerous times in the wild.
This problem occurs when your website’s “WWW” version does not redirect to the “non-WWW” version.
Switching your site to HTTPS can also occur without redirecting the HTTP site. In short, all your site’s versions should be in the same place.

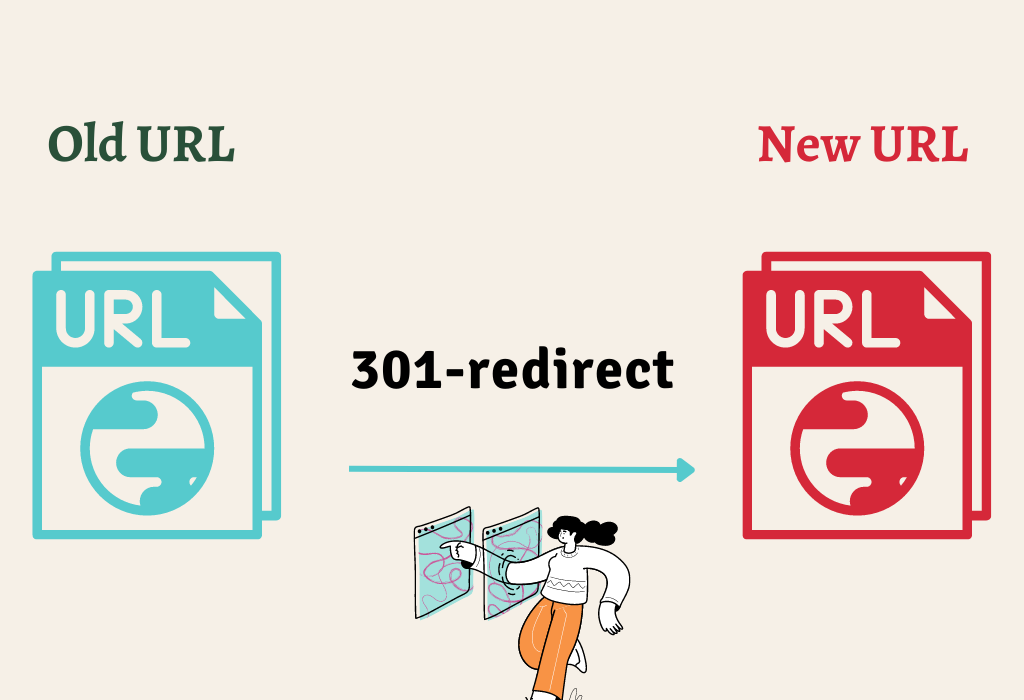
- Using a 301 Redirect
A 301 redirect is the most effective way to combat duplicate content issues by specifying which duplicates are the “correct” for search engines to index and rank. It’s an instruction from your web server that tells it to direct any visitors who land on a certain page (the “duplicate”) to another page instead (the “original”).
This ensures that only a one-page version will be indexed, eliminating potential conflicts between multiple versions of the same content and avoiding confusion for search engine crawlers. As a bonus, this method also passes link equity from the duplicate pages to their original counterparts, boosting rankings and visibility even further.
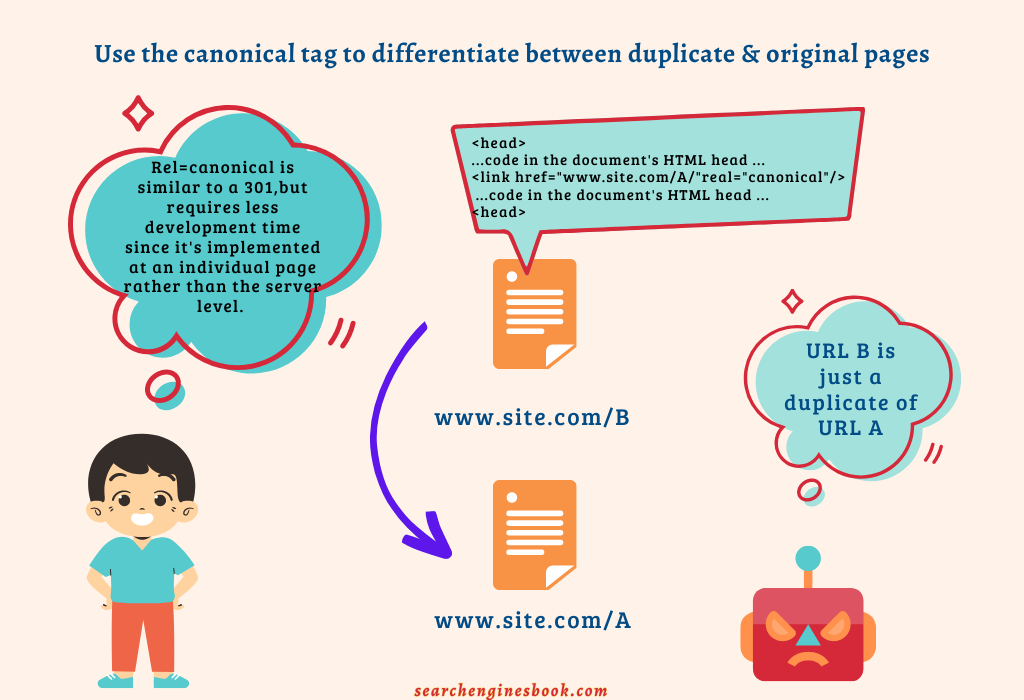
- The rel=canonical Attribute
If you don’t want or can’t use a 301 redirect, then using the rel=”canonical” attribute is an alternative solution for dealing with duplicate content issues. This HTML tag helps inform search engines which version should be treated as though it were a copy of another URL – all links, metrics, and ranking power attributed to this specified URL are credited back up into its canonical source.
In other words, it allows you to consolidate multiple pages with similar content into one page without creating competition between them or diluting relevancy signals across several different URLs; instead, they combine for greater overall impact.
- Parameter Handling Tool in Google Search Console:
The third option available when tackling duplicate content problems is through the parameter handling tool within Google Search Console – here, you can set parameters such as session IDs or tracking codes so that these are ignored by search engine crawlers when crawling your website’s pages, thus preventing duplication from occurring in the first place.
With this tool, you can specify whether certain URLs should be crawled at all times (or not) depending on what type of data they contain – giving complete control over how much information gets indexed and ranked by Google’s algorithms when determining SERP results.
How to Avoid Duplicate Content Issues?
Duplicate content is a major issue for webmasters, as it can lead to penalties from search engines. Duplicate content occurs when two or more pages on the same website contain similar or identical content.
Using Canonical Tags
One way to avoid having duplicate content issues is by using canonical tags when publishing new web pages or blog posts. A canonical tag tells search engines which version of a webpage should be indexed so that any other copies are ignored and do not affect SEO performance negatively.
It also helps ensure clarity among users who might otherwise land on multiple pages containing identical information but with slightly different URLs (e.g., www vs. http).
Proper Internal Linking
Another way to reduce duplication issues is through proper internal linking practices within a website’s architecture structure. This ensures each page has unique links pointing towards it rather than relying solely upon external links for SEO value.
Additionally, this prevents crawling bots from getting stuck in an infinite loop where they continually crawl between two pages without ever reaching another destination URL elsewhere within the domain/website hierarchy structure itself.
Taxonomy
As a starting point, examining your site’s taxonomy is prudent. Whether you’re working on a new or existing document, mapping out the pages from a crawl and assigning a unique H1 and focus keyword is a great place to start. Organizing your content into topic clusters can assist you in developing a well-thought-out strategy that minimizes duplication.
Check Plagiarism
You should always check for plagiarism before publishing new written work online. This ensures that none of your material appears anywhere else on the internet without permission being granted first.
Search Engine Algorithms
Search engines are designed to provide users with unique and relevant query results. When duplicate content exists on multiple pages, search engine algorithms may not know which version should be indexed in the SERPs (search engine result pages). As a result, they may choose not to index any of them at all – leading to decreased visibility and traffic for your site.
To avoid duplicate content issues, ensure all pages on your website are unique and original. If you must use the same material (such as quotes), attribute it properly and link back to its source.
What Are Multiple Site Issues?
Multiple site issues occur when two or more websites contain similar or identical content without proper attribution or linking to the source.
Confusion For User And Search Engine
Multiple site issues can confuse users and search engines as they try to determine which site should be ranked higher in search results.
For example, if two sites have an article about SEO best practices, but neither links back to the other, it’s difficult for a user and search engine to know which one is the authoritative source. In this case, both sites could suffer from lower rankings due to duplicate content.
Keyword Cannibalization
Another issue that arises with multiple sites is keyword cannibalization. If two pages on different websites target the same keyword phrase, both will compete against each other for ranking in SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages).
This can result in both pages ranking well since they compete against each other instead of focusing on outranking external competitors.
Multiple site issues can be complex, but they are important regarding SEO and website usability.
How Can You Resolve Multiple Site Issues?
Duplicate content can be a major website issue, especially when multiple sites are involved. This includes both text-based and image-based duplicates. When search engines crawl these pages, they may need to know which version should be indexed first in their results pages leading to confusion about which page should rank higher.
By understanding the causes and implications of multiple site issues, you can take proactive steps to resolve them.
Finding Duplicate Content
Finding Duplicate Content Within Your Website
You can easily find duplicate content with ContentKing by checking whether your pages have a unique page title, meta description, and H1 heading. You can do this by opening the “Meta information” and “Content Headings” cards in the Issues section. Check to see if there are any outstanding issues with the following:
The Index Coverage report in Google Search Console is also useful for identifying duplicate content on your site. Keep an eye out for the following issues:
Duplicate without user-selected canonical: Google discovered duplicate URIs not canonicalized to a preferred version.
Duplicate, Google chose a different canonical than the user: Google chose to ignore your canonical on URLs found on their own and instead assigns Google-selected canonicals.
Duplicate, submitted URL not selected as canonical: Google disregarded the canonicals you specified for URLs submitted via an XML sitemap.
Finding Duplicate Content Outside Your Website
If you have a small website, you can try searching for phrases between quotes in Google. For example, to see if there are any other versions of this article, I could search for “Using ContentKing, you can easily find duplicate content by checking whether your pages have a unique page title, meta description, and H1 heading.”
For larger websites, you can also use a service like Copyscape. Copyscape searches the web for multiple instances of the same or nearly identical content.
What If My Content Has Been Copied Against My Will?
What should you do if your content has been copied and you have yet to use a canonical tag to indicate that it is the original?
FAQs About Duplicate Content and Multiple Site Issues
Conclusion
In conclusion, duplicate content and multiple site issues can have a negative impact on your website’s search engine rankings. It is important to understand the potential risks of these issues and take steps to prevent them from occurring.
By following best practices such as avoiding duplicate content, using canonical tags, and monitoring multiple sites with similar URLs or content, you can ensure that your website remains in good standing with search engines. Taking the time to address any existing duplicate content & multiple site issues now can save you time and money down the road to optimizing your website for SEO success.
Do you want to ensure your website is optimized for search engine visibility? Don’t let duplicate content or multiple site issues keep you from ranking high. Take control of your online presence and ensure that all the hard work you put into creating a great user experience pays off. Invest in SEO services today and get ahead of the competition!
